之前的文章分别使用动态代理详解自定义Spring中MySQL数据库的事务以及使用aop配置实现自定义的MySQL事务管理,这两个都是使用了自己编写的事务管理器,可谓是“自己动手丰衣足食”。实际上,Spring框架本身就给我们提供了强大的事务管理器,可以不用我们自己手动写事务管理器就可以实现对数据库操作的事务管理。下面边开始实现对事务管理的配置:
首先建立数据库以及用户表:
create database if not exists springdemo;
use springdemo;
create table if not exists Account(id int(4) auto_increment primary key,name varchar(16) not null,password varchar(16) not null,age int(3) ,createtime datetime default now(),money int(8));1.测试项目的整体目录
2.pom.xml的依赖配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springdemo11</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<!-- 引入MySQL数据库依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.21</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入Spring核心包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入c3p0数据源依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mchange</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.5.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入测试依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入切aop依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入spring-jdbc依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>3.测试项目的代码
package dao;
import entity.Account;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Classname:springdemo3
*
* @description:{description}
* @author: 陌意随影
* @Date: 2020-08-01 17:32
*/
public interface AccountDao {
/**
* @Description :保存用户
* @Date 11:51 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param account :
* @return boolean
**/
public boolean saveAccount(Account account);
/**
* @Description :更新用户
* @Date 11:51 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param newAccount :
* @return boolean
**/
public boolean updateAccount(Account newAccount);
/**
* @Description :通过ID删除用户
* @Date 11:52 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param id :
* @return boolean
**/
public boolean deleteAccountById(int id);
/**
* @Description :通过ID查询用户
* @Date 11:52 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param id :
* @return entity.Account
**/
public Account findAccountById(int id);
/**
* @Description :查找所有用户
* @Date 11:52 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param :
* @return java.util.List<entity.Account>
**/
public List<Account> findAll();
}package dao;
import entity.Account;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Classname:AccountDaoImpl
*
* @description:AccountDao的实现类
* @author: 陌意随影
* @Date: 2020-08-01 17:32
* @Version: 1.0
**/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
//用于进行MySQL增删查改
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = null;
/**
* @Description :方便在配置文件中注入JdbcTemplate对象
* @Date 12:16 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param queryRunner :
* @return void
**/
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
/**
* @Description :保存用户
* @Date 12:17 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param newAccount :
* @return boolean
**/
public boolean saveAccount(Account newAccount) {
return jdbcTemplate.update("insert into account(name,password,age,createTIme,money) values(?,?,?,?,?)",
newAccount.getName(),newAccount.getPassword(),
newAccount.getAge(),newAccount.getCreateTime(),newAccount.getMoney())== 1;
}
/**
* @Description :更新用户
* @Date 12:18 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param newAccount :
* @return boolean
**/
public boolean updateAccount(Account newAccount) {
return jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name=?,password=?,age=?,createTime=?,money=? where id=?",
newAccount.getName(),newAccount.getPassword(),
newAccount.getAge(),newAccount.getCreateTime(),newAccount.getMoney(),newAccount.getId())==1;
}
/**
* @Description :通过ID删除用户
* @Date 12:18 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param id :
* @return boolean
**/
public boolean deleteAccountById(int id) {
return jdbcTemplate.update("delete from account where id=?",id) == 1;
}
/**
* @Description :通过ID查询用户
* @Date 11:02 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param id :
* @return entity.Account
**/
public Account findAccountById(int id) {
List<Account> list = jdbcTemplate.query("select* from account where id=?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), id);
if (list.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
if (list.size()==1){
return list.get(0);
}
return null;
}
/**
* @Description :查询所有哟用户
* @Date 11:01 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param :
* @return java.util.List<entity.Account>
**/
public List<Account> findAll() {
return jdbcTemplate.query("select* from account",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class));
}
}package entity;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Classname:Account
*
* @description:
* @author: 陌意随影
* @Date: 2020-08-01 17:33
* @Version: 1.0
**/
public class Account {
//用户主键ID
private int id;
//用户名
private String name;
//用户密码
private String password;
//用户年龄
private int age;
//用户创建时间
private Date createTime ;
//用户的余额
private int money;
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", createTime=" + createTime +
", monney=" + money +
'}';
}
}package service;
import entity.Account;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Classname:springdemo3
*
* @description:{description}
* @author: 陌意随影
* @Date: 2020-08-01 17:35
*/
public interface AccountService {
/**
* @Description :保存用户
* @Date 11:51 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param account :
* @return boolean
**/
public boolean saveAccount(Account account);
/**
* @Description :更新用户
* @Date 11:51 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param newAccount :
* @return boolean
**/
public boolean updateAccount(Account newAccount);
/**
* @Description :通过ID删除用户
* @Date 11:52 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param id :
* @return boolean
**/
public boolean deleteAccountById(int id);
/**
* @Description :通过ID查询用户
* @Date 11:52 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param id :
* @return entity.Account
**/
public Account findAccountById(int id);
/**
* @Description :查找所有用户
* @Date 11:52 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param :
* @return java.util.List<entity.Account>
**/
public List<Account> findAll();
/**
* @Description :从用户ID为sourceId的用户向用户ID为targetId的用户转账money
* @Date 11:55 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param sourceId
* @param targetId
* @param money :
* @return boolean
**/
public boolean tranferMoney(int sourceId,int targetId,int money);
}package service;
import dao.AccountDao;
import entity.Account;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Classname:AccountServiceImpl
* @description:
* @author: 陌意随影
* @Date: 2020-08-01 17:35
* @Version: 1.0
**/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
//用户数据可访问的Dao接口
private AccountDao accountDao;
/**
* @Description :方便在配置文件中注入AccountDao的实现了AccountDaoImpl
* @Date 12:21 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param accountDao :
* @return void
**/
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public boolean saveAccount(Account account) {
return accountDao.saveAccount(account);
}
public boolean updateAccount(Account newAccount) {
return accountDao.updateAccount(newAccount);
}
public boolean deleteAccountById(int id) {
return accountDao.deleteAccountById(id);
}
public Account findAccountById(int id) {
return accountDao.findAccountById(id);
}
public List<Account> findAll() {
return accountDao.findAll();
}
/**
* @Description :从用户ID为sourceId的用户向用户ID为targetId的用户转账money
* @Date 11:55 2020/8/9 0009
* @Param * @param sourceId
* @param targetId
* @param money :
* @return boolean
**/
public boolean tranferMoney(int sourceId, int targetId, int money) {
//获取sourceId对应的用户
Account sourceAccount = this.findAccountById(sourceId);
//获取targetId对应的用户
Account targetAccount = this.findAccountById(targetId);
//转账失败
if (sourceAccount == null || targetAccount == null) {
return false;
}
//转账者扣去转账的金额
sourceAccount.setMoney(sourceAccount.getMoney() -money);
//目标对象加上获取的转账金额
targetAccount.setMoney(targetAccount.getMoney()+money);
//更新转账者的账户
boolean b = this.updateAccount(sourceAccount);
//模拟异常
// int i = 1/0;
//更新转账目标者的账户
boolean b1 = this.updateAccount(targetAccount);
return b == true && b1 == true;
}
}4.测试代码
package test;
import entity.Account;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import service.AccountService;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Classname:AccountTest
*
* @description:
* @author: 陌意随影
* @Date: 2020-08-01 17:39
* @Version: 1.0
**/
public class AccountTest {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private AccountService accountService;
@BeforeEach
public void init(){
applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
System.out.println("启动");
}
@AfterEach
public void destroy(){
}
@Test
public void testSave(){
Account account = applicationContext.getBean("account", Account.class);
account.setAge(434);
account.setName("李四");
account.setPassword("打个卡的撒老顾客");
account.setCreateTime(new Date());
account.setMoney(1000);
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
boolean fla = accountService.saveAccount(account);
System.out.println("插入用户:"+fla);
}
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
Account account = applicationContext.getBean("account", Account.class);
account.setAge(77);
account.setName("站干啥");
account.setPassword("54545");
account.setCreateTime(new Date());
account.setId(3);
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
boolean fla = accountService.updateAccount(account);
System.out.println("更新用户:"+fla);
}
@Test
public void testDelete(){
Account account = applicationContext.getBean("account", Account.class);
account.setId(5);
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
boolean fla = accountService.deleteAccountById(account.getId());
System.out.println("删除用户:"+fla);
}
@Test
public void testFindOne(){
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
Account account1 = accountService.findAccountById(6);
System.out.println("查找单个用户"+account1);
}
@Test
public void testFindAll(){
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
List<Account> accountList = accountService.findAll();
for (Account a :accountList) {
System.out.println(a);
}
}
@Test
public void testTran(){
//获取没有经过事务管理的普通AccountServiceImpl
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
accountService.tranferMoney(3,6,100);
}
}5.bean.xml的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 配置实体类 -->
<bean id="account" class="entity.Account" scope="prototype"></bean>
<!-- 配置AccountDaoImpl-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="dao.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- 注入jdbcTemplate-->
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置jdbcTemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置c3p0数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!-- 用户名-->
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<!-- 数据库驱动-->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<!-- 密码-->
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
<!-- URL-->
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdemo?serverTimezone=UTC"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置AccountServiceImpl-->
<bean id="accountService" class="service.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 注入accountDao-->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- 配置事务通知 -->
<tx:advice id="transactionInterceptor" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!-- 配置事务的属性 -->
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 配置方法的属性,其中“*”表示任意,比如说save*表示以save开头的所有方法,比如saveAccount,saveUser等。。-->
<tx:method name="tranferMoney" isolation="DEFAULT" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="save*" isolation="DEFAULT" read-only="false"></tx:method>
<tx:method name="update*" isolation="DEFAULT" read-only="false"></tx:method>
<tx:method name="delete*" isolation="DEFAULT" read-only="false"></tx:method>
<tx:method name="find*" isolation="DEFAULT" read-only="true" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"> </property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置aop-->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切入点表达式-->
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* *service.AccountServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!-- 建立切入点表达式和事务通知的对应关系-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="transactionInterceptor" pointcut-ref="pt"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
</beans>tx:method 的属性详解: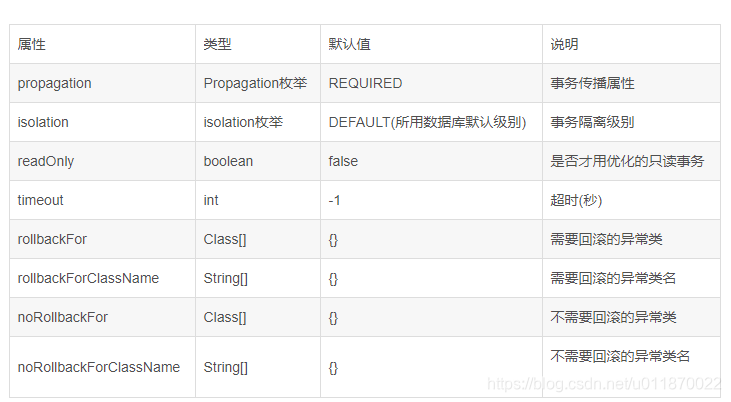
readOnly:
事务属性中的readOnly标志表示对应的事务应该被最优化为只读事务。如果值为true就会告诉Spring我这个方法里面没有insert或者update,你只需要提供只读的数据库Connection就行了,这种执行效率会比read-write的Connection高,所以这是一个最优化提示。在一些情况下,一些事务策略能够起到显著的最优化效果,例如在使用Object/Relational映射工具(如:Hibernate或TopLink)时避免dirty checking(试图“刷新”)。
timeout:
在属性中还有定义“timeout”值的选项,指定事务超时为几秒。一般不会使用这个属性。在JTA中,这将被简单地传递到J2EE服务器的事务协调程序,并据此得到相应的解释。
Isolation Level(事务隔离等级)的5个枚举值
为什么事务要有Isolation Level这个属性?先回顾下数据库事务的知识:
第一类丢失更新(lost update):在完全未隔离事务的情况下,两个事物更新同一条数据资源,某一事物异常终止,回滚造成第一个完成的更新也同时丢失。
第二类丢失更新(second lost updates):是不可重复读的特殊情况,如果两个事务都读取同一行,然后两个都进行写操作,并提交,第一个事务所做的改变就会丢失。
脏读(dirty read):如果第二个事务查询到第一个事务还未提交的更新数据,形成脏读。因为第一个事务你还不知道是否提交,所以数据不一定是正确的。
虚读(phantom read):一个事务执行两次查询,第二次结果集包含第一次中没有或者某些行已被删除,造成两次结果不一致,只是另一个事务在这两次查询中间插入或者删除了数据造成的。
不可重复读(unrepeated read):一个事务两次读取同一行数据,结果得到不同状态结果,如中间正好另一个事务更新了该数据,两次结果相异,不可信任。
当遇到以上这些情况时我们可以设置isolation下面这些枚举值:
DEFAULT:采用数据库默认隔离级别
SERIALIZABLE:最严格的级别,事务串行执行,资源消耗最大;
REPEATABLE_READ:保证了一个事务不会修改已经由另一个事务读取但未提交(回滚)的数据。避免了“脏读取”和“不可重复读取”的情况,但是带来了更多的性能损失。
READ_COMMITTED:大多数主流数据库的默认事务等级,保证了一个事务不会读到另一个并行事务已修改但未提交的数据,避免了“脏读取”。该级别适用于大多数系统。
READ_UNCOMMITTED:保证了读取过程中不会读取到非法数据。隔离级别在于处理多事务的并发问题。
关于propagation属性的7个传播行为
REQUIRED:指定当前方法必需在事务环境中运行,如果当前有事务环境就加入当前正在执行的事务环境,如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务。这是默认值。
SUPPORTS:指定当前方法加入当前事务环境,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。
MANDATORY:指定当前方法必须加入当前事务环境,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。
REQUIRES_NEW:指定当前方法总是会为自己发起一个新的事务,如果发现当前方法已运行在一个事务中,则原有事务被挂起,我自己创建一个属于自己的事务,直我自己这个方法commit结束,原先的事务才会恢复执行。
NOT_SUPPORTED:指定当前方法以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起,等我以非事务的状态运行完,再继续原来的事务。
NEVER:指定当前方法绝对不能在事务范围内执行,如果方法在某个事务范围内执行,容器就抛异常,只有没关联到事务,才正常执行。
NESTED:指定当前方法执行时,如果已经有一个事务存在,则运行在这个嵌套的事务中.如果当前环境没有运行的事务,就新建一个事务,并与父事务相互独立,这个事务拥有多个可以回滚的保证点。就是指我自己内部事务回滚不会对外部事务造成影响,只对DataSourceTransactionManager事务管理器起效。
注意:

其中第一个" * "代表返回值,第二个" * " 第表示代表任意目录下的service包,第三个 “ * ”代表方法名,“(..)”代表任意方法参数。
6.测试
笔者经过测试,运行无误。有需要的可自行下载源代码后进行测试。本项目的源代码已经上传到个人博客,如有需要请自行下载:http://moyisuiying.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/springdemo11.rar











